Hello, guys, In today’s article we will study paramecium. Like – what is paramecium? Where is found paramecium? Classification of Paramecium, We will know the answers to many such questions today, so let’s start.
What is a paramecium?
Paramecium is a typical ciliate and is placed in the subphylum Ciliophora of the phylum Protozoa. The specialty of ciliate animals is the presence of cilia which act as moving organs. Two types of nuclei are found in all ciliate animals, which are called Macronucleus and Micronucleus.
Hence they show nuclear dimorphism. The number of micronuclei may be one or more in different species. For example, P. caudatum has one, large and well-shaped micronuclei. P. aurelia has two micronuclei. Whereas P. multimicronucleatum has many micronuclei.
The genus Paramecium is a monotypic ciliate with 10 known species. P. bursaria is green due to the presence of the symbiotic algae Zoochlorella.
Where is found paramecium?
Paramecium is found in ponds, ponds, lakes and rivers. These are found in large numbers in clean water bodies along with decaying organic matter.
Classification of Paramecium –
Paramecium caudatum
| Phylum | Protozoa |
| Subclass | Ciliophora |
| Class | Ciliata |
| Subclass | Holtrichia |
| Order | Hymenostomatida |
| Suborder | Peniculina |
| Genus | Paramecium |
| Species | caudatum |
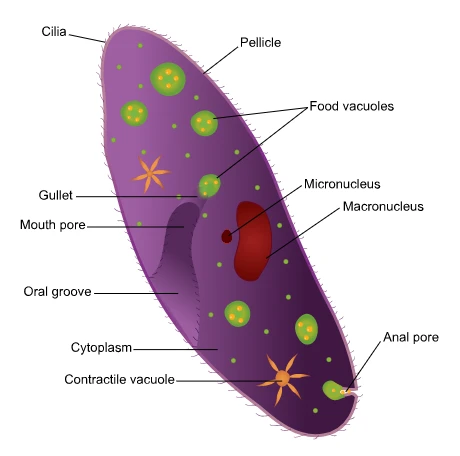
What is the Structure of Paramecium?
Paramecium size and shape –
Paramecium is a single-celled microorganism. Its size varies in different species. Paramecium caudatum has a size of 170 – 290 microns, and P. aurelia has a size of 120-250 microns. Paramecium is an elongated, slipper-shaped animal. Generally, it is also called Slipper animalcule. Their body is asymmetric with a flattened oval or ventral and a convex distal or dorsal surface. The front end of Paramecium is spherical and the rear end is thick and cone-shaped.
The structure of Paramecium is quite complex due to some developed organs. The following main organs can be described below.
Pellicle –
The body of Paramecium is surrounded by a thin, strong, and flexible membrane, which is called a pellicle. It gives a definite shape to the body of the organism. The pellicle is divided into polygonal or rhomboid depressions with raised margins.
A cilium emerges from the center of each hexagonal region. From the polygonal regions emerge a regular series of similar cavities, follicles, and cilia. The anterior and posterior margins of the trichocyst bear pores of trichocysts.
Pellicle is made of three membranes. There is an outer membrane or surface membrane along with cilia around the membrane. Alveoli are packed closely together under the outer membrane. These are mostly in flat form. The outer and inner membranes of the alveoli form the inner and middle membranes of the pellicle.
Paramecium Cilia –
Cilia are like hair. It covers the entire body surface of Paramecium (Paramecium in Hindi) uniformly. These come out from the center of the alveoli. Some terminal cilia that are long are called Caudal Tuft. Except these, all others are of similar size.
Ultrastructure of cilia –
Each cilium is composed of a fluid matrix and is surrounded by a membrane covering. There is a continuous membranous covering of the pellicle along the outer membrane. There are nine peripheral longitudinal fibers and two central longitudinal fibers inside the matrix.
Each filament is made up of two subfilaments. One of which has a double row of short arms running in the same direction. The central filament is single and attached to an internal membranous sac. There are 9 very sensitive accessory or radial fibers between the central and peripheral fibers.
Oral groove –
In Paramecium, there is a clear, shallow buccal groove on the ventral surface. The oral groove has a long oblique and a conical funnel-shaped pit at the back, which is called a vestibule. The vestibule leads into the oral cavity, a wide tubular passage. It opens into a wide cytopharynx through an oval cytostome. The cytopharynx forms a food vacuole at its near end.
Cilia in the oral groove show diversity in shape and arrangement. Cilia in the oral groove show variation in size and arrangement. These form the following structures.
Endoral membrane –
Specialized cilia in the buccal cavity combine in a crescent-shaped manner to form the endocrine membrane. It runs transversely and is located at the junction of the vestibule and the oral cavity.
Penniculi –
Here two paniculi are located in the left wall of the oral cavity. Each has four rows of cilia. The dorsal panicle is long and crosses the right wall into the cytostome. It ends on the right wall of the cytopharynx. The ventral panniculus is short, and ends at the cytostome. The cilia of the dorsal and ventral panniculi beat in opposite directions.
Quadrulus –
It is also made up of four rows of cilia. It runs along the dorsal wall of the oral cavity, passes to the right near the cytostome, and ends near the end of the dorsal paniculate.
Friends, I hope this article helps you understand what is Paramecium. You might have liked the information given about (What is paramecium in Hindi), if you liked it then please share it as much as possible.
Thank you
Nice post. I was checking this weblog continuously and I’m impressed!
Beneficial information specifically the last section 🙂 I take care of
such info much. I used to be seeking this particular
info for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
Thanks and Welcome to you