“Friends, just as in our daily life we use a dozen for 12 items, a gross for 144 items, and a ring for 500 items, similarly, the term ‘mole‘ is used for extremely tiny particles. Friends, atoms, and molecules are extremely tiny particles, and even in the smallest amount of substance, their number is very large. The unit of mole is used to express this large number. This term is derived from the Latin word ‘mole’ which means a heap or accumulation. It was first used by Wilhelm Ostwald in 1894.
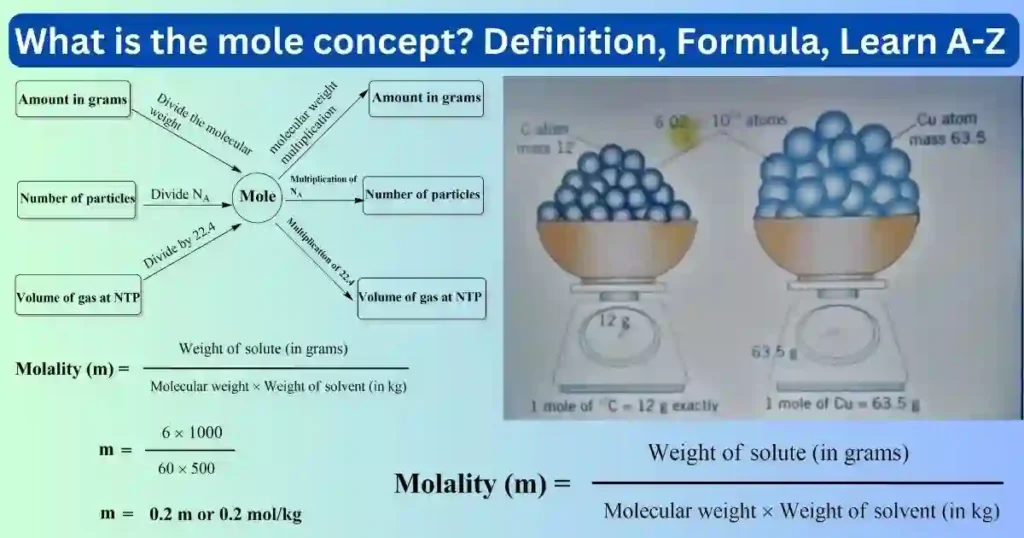
What is the mole concept?
The size of atoms and molecules is very small, and even in a very small quantity of a substance, their number is quite large. To express this number, a unit is needed. Just as we use grams as the unit for mass and meters as the unit for length, similarly, the mole unit is used for the quantity of a substance.
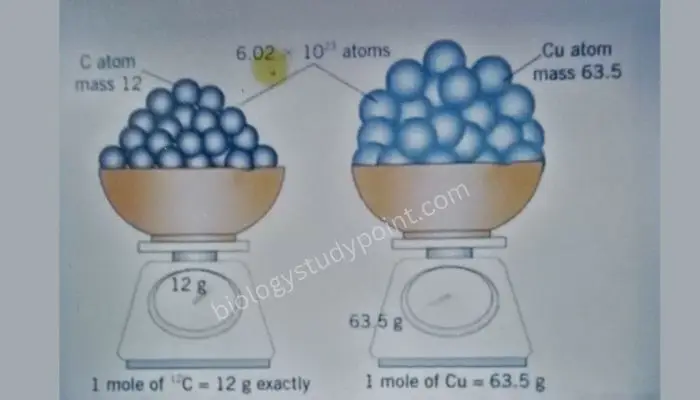
The quantity of a substance in which there are as many particles as there are carbon -12 atoms in exactly 12 grams is called the number of particles in one mole.
A quantity of a substance in which there are 6.022×1023 fundamental particles is called one mole of the substance. The number of particles in one mole is called Avogadro’s number, represented by NA.
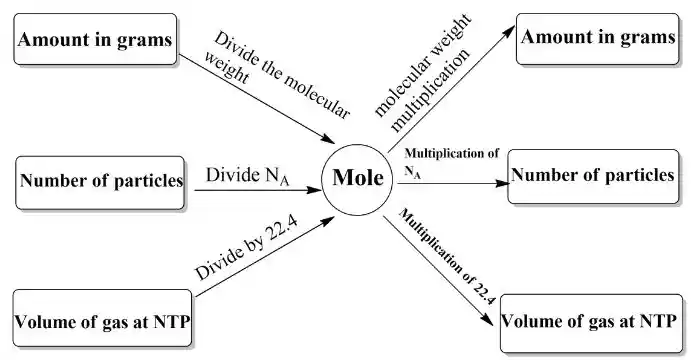
Mole Concept-Related Important Formulas
What is molar mass?
In simple terms, the molar mass of a substance refers to the mass of one mole of that substance. It is expressed in grams per mole. The molar mass in grams per mole numerically equals the atomic, molecular, or formula mass.
For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is 18.02 grams/mole.
The molar mass of NaCl is 58.5 grams/mole.
Note – Just as in the mole concept, where only moles are used in place of gram atoms, gram molecules, and gram ions, similarly, in molar mass, the molar mass is used in place of atomic mass, molecular mass, and formula mass.
Q. What will the number of 80 grams of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) moles?
n = ?, w = 80 g
NaOH = 23+16+1= 40
n = w/m
n = 80/40
n = 2
Percentage composition –
The percentage amount of elements present in a compound is called percentage composition.
Formula = mass of elements present in the compound/molar mass of the compound
Example.
H2O – H = 2
atomic weight = 18
2X100/18 = 100/9 = 11.11%
Formula, structure formula, molecular formula, and empirical formula.
What is Formula?
The group of symbols that represent a molecule of a substance is called a formula.
For example, the formula of water is H2O, the formula of calcium carbonate is CaCO3, and the formula of sucrose is C12H22O11.
Structure formula:
The chemical formula of a compound which shows the arrangement of various atoms present in it is called structural formula.
Like the structural formula of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) –
H-O-O-H
What is the molecular formula?
The formula of a compound that shows the actual number of different atoms present in its molecule is called molecular formula.
Just as hydrogen peroxide has H2O2, similarly glucose has C6H12O6.
What is an empirical formula?
The simple formula of a compound which expresses the number of atoms of different elements present in the molecule of that compound i.e. the best whole number ratio of atoms is called the empirical formula.
- To find the basic proportional formula from the percentage composition – Based on the composition of the compound, its basic proportional formula can also be found. For this, the following terms are used.
- Step 1- The percentage of each element is divided by its atomic weight, this gives the mole number of each element.
- Step 2- All the numbers obtained are divided again by the smallest number among them, this gives a simple ratio of the mole number.
- Step 3 – By taking the symbols of an element close to each other and writing their simple mole number on the right side below them, the empirical formula is obtained. Therefore, to find the proportional formula of the compound, we should know about its weight composition and the elements present in it.
How to Calculate the Molecular Formula?
- The relationship between the atomic formula and the empirical formula is as follows:
- Atomic formula = (empirical formula) × n
- Where n = atomic weight / empirical formula weight
- Empirical formula weight = sum of atomic weights of all atoms represented by the empirical formula
Question. An inorganic compound contains 56.53 percent potassium, 8.69% carbon, and 34.78% oxygen. Its molar mass is 138 grams. Then find its proportional formula and molecular formula.
| Element | Percentage of element | Atomic mass | Relative number = percent atoms + mass | Simplest atomic ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium (K) | 56.53 | 39 | 56.53+39 = 1.449 | 1.449/0.724 = 2.0 |
| Corban (C) | 8.69 | 12 | 8.69+12 = 0.724 | 0.724/0.724 = 1.0 |
| Oxygen (O) | 34.78 | 16 | 34.78+16 = 2.173 | 2.173/0.724 = 3.0 |
The simplest ratio of elements in the compound = 2:1:3
Therefore, the empirical formula of the compound is K2CO3.
Empirical Formula mass:
K2CO3 = 2(39) + 12 + 3(16) = 138 grams
Molar Mass = 138 gm
n = molar mass / empirical formula weight = 138/138 = 1
Therefore, the molecular formula of the compound is K2CO3.
Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry or mole ratio is the branch of chemistry that calculates the quantities of reactants involved in chemical reactions, as well as the masses and volumes of products produced.
Limiting Reactants in Chemical Reactions:
Sometimes, the quantity of reactants present in chemical reactions is not enough to complete the balanced reaction. In such situations, the quantity of one reactant is greater than the quantity required for a balanced reaction, limiting the production of products.
Q. Magnesium oxide is obtained by burning 1 gram of magnesium in 0.5 gram of oxygen. The limiting reagent in this reaction can be calculated as follows.

Therefore, if 48 grams of magnesium reacts with 32 grams of oxygen, then 1 gram of magnesium will react with = 32/48 = 0.67 g of oxygen. However, in reality, only 0.5 grams of oxygen is available.
In other words, the actual amount of oxygen is less than the amount available for the reaction, so oxygen is the limiting reagent in the reaction.
Reactions in solutions:
- Mass percentage (w/w%)
- Mole fraction
- Molarity
- Molality
Mass – Mass Percentage (w/w%) –
The number of parts by weight of a solute present in 100 parts by weight of a solution is called the mass percentage of the solute.
Formula –
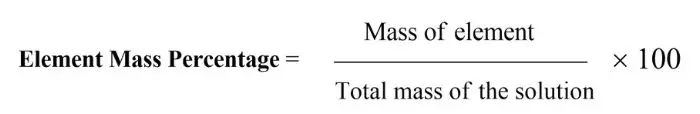
For example – 5gm NaCl dissolved in 500gm of solution. Calculate the percentage.
5×100/500 = 1%
Mole fraction:
The ratio of the number of moles of a component in a solution to the total number of moles present in the solution is called the mole fraction of that component.
Suppose two components A and B are present in a solution, its number of moles are na and nb respectively, and mole fraction are xa and xb respectively.
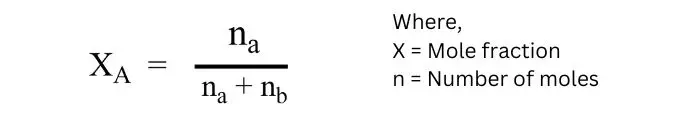
Molarity:
The number of moles of solute present in one liter of solution is called the molarity of that solution.
Formula –
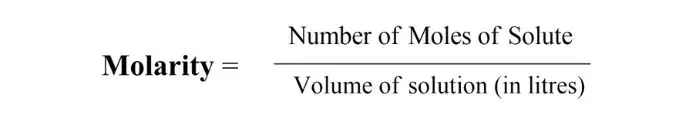
If in milliliters (ml), multiply by 1000.
The unit of molarity is mol/L.
Q. Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 5 grams of sodium chloride in 2 liters of solution when the molecular weight of sodium chloride is 58.5 g/mol.
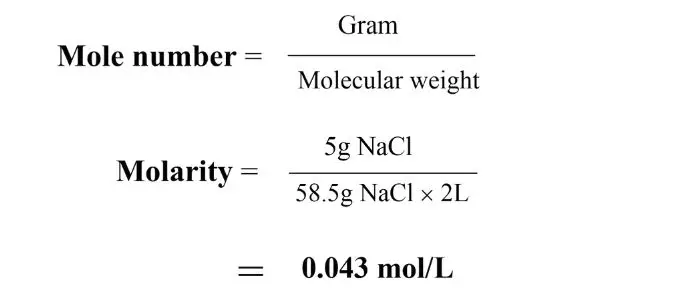
What is Molality?
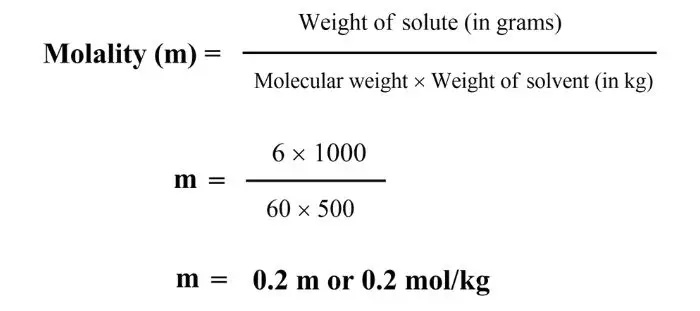
The number of moles of a solute in 1 kg of solvent is called molality and is expressed as ‘m’.
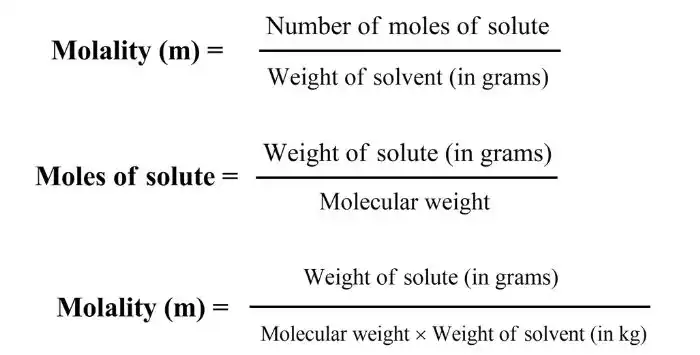
Q. 6 grams of urea (NH2-CO-NH2) is dissolved in 500 grams of water, then find the molarity.
What is molar mass?
Molar Mass –
The mass of 1 mole of any substance. Its molar mass is called which is denoted by “M”, whose unit is gm/mole.
Molar mass expressed in grams is numerically equal to the molecular mass or mass of the formula. As –
M CO2 = molecular mass of CO2
M CO2 = mass of CO2 formula
M CO2 = Molar mass of CO2
M CO2 = CO2
= 12+32 = 44 grams/mol
What is a gram’s atomic mass?
Gram Atomic Mass –
Gram atomic mass or 1 gram atom is the mass of 6.022×1023 atoms of an element which is expressed in grams.
Example – Gram atomic mass of sodium (Na) or 1 gram atom of sodium (ie 23 grams Na) is the mass of atoms in 1 mole of sodium.
Generally, we can express it as follows.
Gram atomic mass = one gram atom = 1 mole atoms = 6.022×1023 atoms
What is gram molecular mass?
Gram Molecular Mass –
Gram molecular mass or 1 gram mole is the mass of 6.022×1023 molecules of a substance (element or compound) which is expressed in grams.
Example – Gram molecular mass of CaCO3 or one gram mole (or 100 grams) of CaCO3 is the mass in grams of 6.022×1023 molecules of CaCO3.
Generally, we can display it as follows.
Gram molecular mass = one gram mole = 1 mole molecule = 6.022×1023 molecules
Normality –
The normality of a substance is the number of gram equivalents that are present in one-liter volume. It is called the normality of that substance. Which is denoted by N.
Number of gram equivalents = e
VL holds solution = e
1L solution holds = e/v
N=e/v
e = w/E
E = equivalent weight of the substance, where w = weight in grams
N=w/E. V[L]
w = N.E V[ml] /1000 Normal = equivalent/litre
Relation between Normality and Molarity –
Let w be the amount of solute present in one milliliter of solution.
W = E N V (c.c) / 1000
= m Mr. V(c.c)/1000
Since the amount of solute is the same. Therefore
E N V (cc) / 1000 = m Mr V (cc) / 1000
N/Mr = m/E = x
x = acidity, basicity, acidity, valence, change in oxidation number, number of cations, number of anions.
m/E = x
E = m/x
Equivalent weight = molecular weight/acidity
Example –
HCl = hydrochloric acid
EHCl = MHCl/x
EHCl = 1+35.5/1
EHCl = 36.5 Ans
H2SO4 = sulfuric acid
EH2SO4 = MH2SO4/x
= 2+32+64/2
= 98/2
= 49 Answers
Stoichiometric Coefficient –
In any balanced chemical equation, the coefficient of the formulas of reactants and products is called a stoichiometric coefficient. As –
2KClO3 ———— 2KCl + 3O2
The stoichiometric coefficient of potassium chlorate is 2 and the stoichiometric coefficient of oxygen is 3.
Parts Per Million (PPM) –
1 Million = 106
When the amount of solute in a solution is much less. So in such a situation, the concentration of the solution is measured in ppm. The number of grams of solute per million of a solution is called PPM.
PPM = Amount of solute ×106/Volume of solution
For example – if NaCl is 10 PPM, then this statement means that 10 grams of sodium chloride is dissolved in 106 grams of solution.
Conclusion
I hope you found this information about mole fractions helpful. If you did, please share it with your friends so they can benefit as well. Thank you!