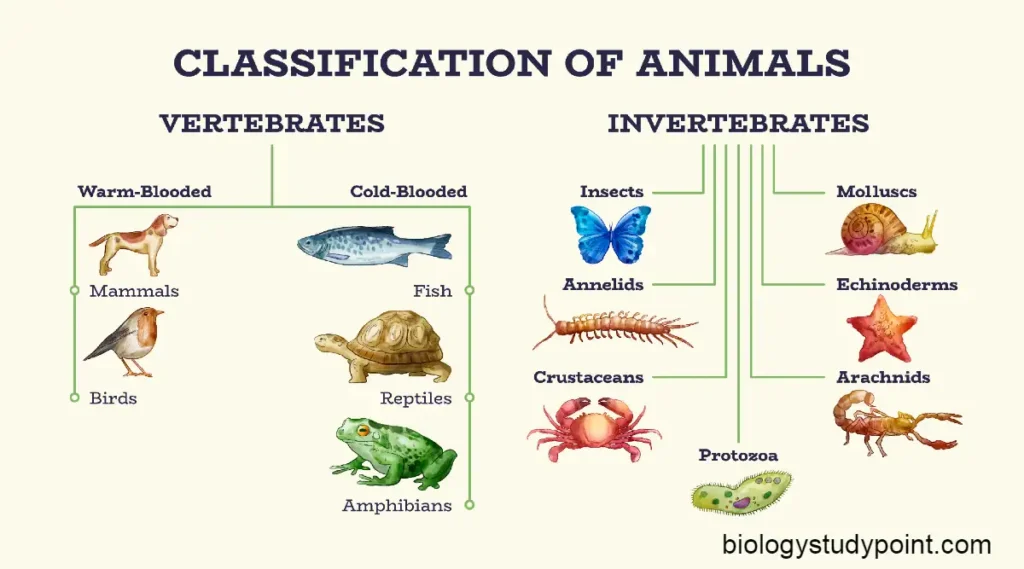
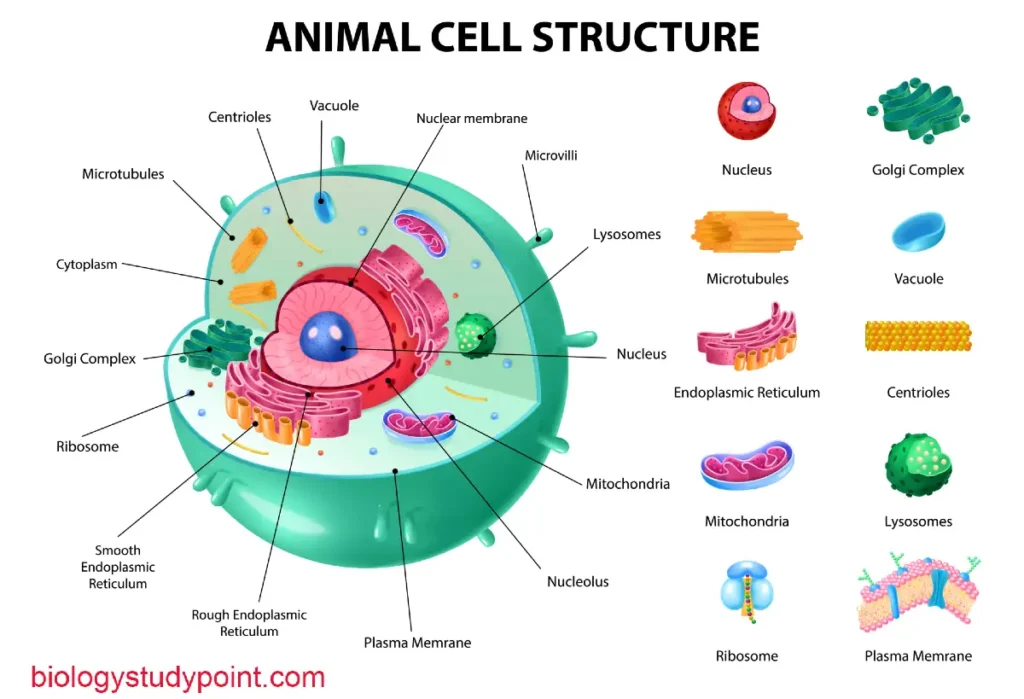
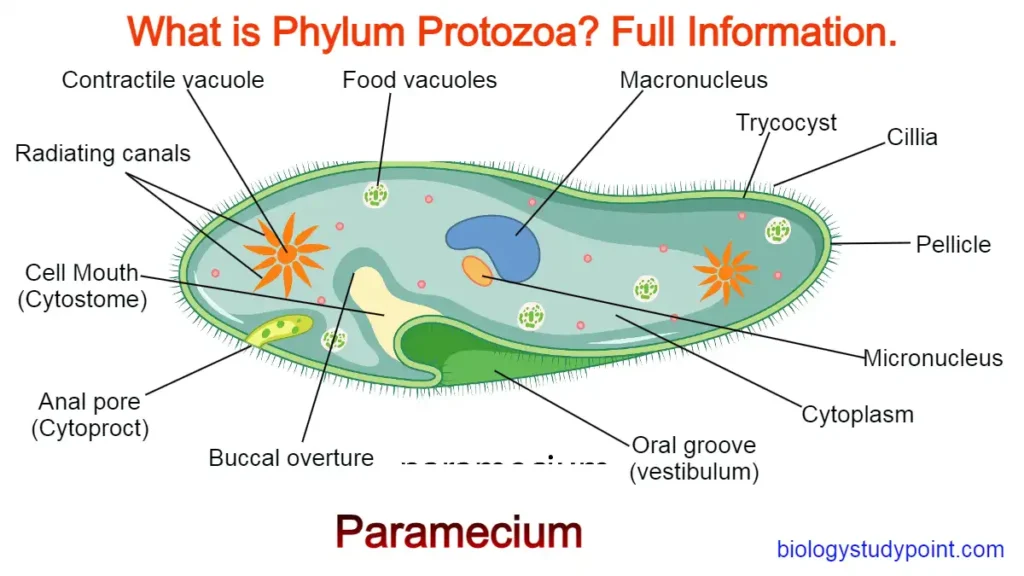
Friends, Do you want to learn about taxonomy and classification from the beginning? If yes, then this article is for you. In it, you will get information related to taxonomy from the beginning. So, let’s start without wasting any time.
What is taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the branch of biology concerned with identifying, naming, and classifying organisms.
For example, if you discover a living being, you observe its special characteristics, essentially making distinctions based on the features you find. Next, you would identify the organism. This might involve studying its cells and determining if it has a cell wall. It also performs photosynthesis, suggesting it’s a plant once you have identified the organism’s name.
There are specific rules for naming, which we will discuss next. Let’s assume you have a name for it now. Finally, a classified organism. Here, we compare it to other plants, looking for similarities and dissimilarities. Based on this comparison, we will assign a taxonomic group.
Friends classification is the most important aspect of taxonomy.
What is Classification?
Classification is the process of grouping organisms based on their similarities and dissimilarities or characteristics.
Hopefully, you have understood the concept. Now, let’s move on.
What is Systematics?
The term systematic was introduced by the scientist Carl Linnaeus. First, let’s clear up the confusion. You might think that systematic and taxonomy are the same, but there is a key difference.
What do we do in taxonomy?
In taxonomy, we identify, characterize names, and classify organisms based on similarities and dissimilarities.
Systematic, however, includes one additional step not found in taxonomy.
Systematics also involve identification, characterization, naming, and classification, similar to taxonomy. However, systematic classification is based on similarity, dissimilarity, and evolutionary relationships. So what extra here? We’ll explore the concept of evolutionary relationships next.
What is Nomenclature?
Giving a scientific name to an organism is called nomenclature. You might wonder why naming is important. Just as we have names to identify each other, organisms need scientific names for clear identification. However, the same organisms might have different names for different religions or languages.
For example, onion is called “kandha” in Maharashtra, kukur for dog in Kolkata, and kalingad for watermelon in Punjab. These local names can confuse.
To avoid this confusion, a living being needed a universally recognized name. This globally accepted name is called a scientific name.
Now, who gives these scientific names?
Scientific names are given according to the rules of the binomial system.
What is binomial nomenclature?
In this method, the scientific name combines two parts: the genus name and the species name.
For example, the scientific name of the frog is Rana tigrina. Here, Rana is the genus name, and Tigrina is the species name.
Who gave us binomial nomenclature?
Scientific scientist Carl Linnaeus introduced this method. In 1751, he published a book called “Philosophia Botanica,” which explains binomial nomenclature. Following that, in 1753, he published another book named “Species Plantarum” classifying 5900 plants. Finally, in 1758, he published another Book titled “Systema Naturae” where he classified 4326 animals.
What are Nomenclature Committees?
These are groups of scientists who name organisms according to the binomial nomenclature system. There are four main committees:
- ICBN – International Code of Botanical Nomenclature (Names Plants)
- ICZN – International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (Names animals)
- ICVN – International Code of Virus Nomenclature (Names viruses)
- ICNB – International Code of Nomenclature Bacteria (Names bacteria)
Now, let’s discuss the rules of binomial nomenclature.
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature:
- The scientific name combines two words: the genus name and the species name.
- The first letter of the genus name is capitalized, while the first letter of the species name is lowercase.
- The scientific name is followed by the abbreviated name of the scientist who first described the organism–for example, Homo sapiens Linn. (Linn. refers to Carl Linnaeus).
- Scientific names are preferably derived from Latin or Greek because these languages are considered “dead,” meaning their meanings are stable and don’t change over time.
- When writing scientific names by hand, underline them, and when printed, they should be italicized.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Organisms are classified in a hierarchical system with different levels called taxonomic ranks. Here’s the order from broadest to most specific:
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
Kingdoms in the Classification System
There are currently more than two kingdoms used to classify organisms. Let’s explore some historical classification systems and their limitations.
Two Kingdoms of Classification
This system, proposed by Carl Linnaeus, divided organisms into two kingdoms: Plantae (plant) and Animalia (animal). The classification was based solely on the presence or absence of a cell wall.
Bacteria, plants, fungi, and algae were placed in the Plantae kingdom. Why? They are kept because the cell wall is found in them, and animals are kept in the Animalia kingdom, where the cell wall is not found.
Limitations of the Two Kingdoms System:
- This system placed unicellular and multicellular organisms together in the Plantae Kingdom.
- It did not account for the fundamental difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What are unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Bacteria, diatoms, dinoflagellates, protozoa, and algae are unicellular organisms, and plants and fungi are multicellular organisms. Another system was developed to correct the mistake that Carl Linnaeus had made.
Three Kingdoms of Classification
This system, introduced by Ernst Haeckel, addressed the issue of unicellular organisms by creating a third kingdom, Protista, to house them.
Limitations of the Three-Kingdom System:
- It grouped prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in the Protista Kingdom.
- Now, on what basis did Hackle divide? Hackle divided based on the organization of the body, meaning that unicellular organisms were picked up and placed in the kingdom Protista.
- He also made a mistake. What was that mistake? He put prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells together. Now, another kingdom system has come to correct this mistake.
Four Kingdoms of Classification
- Scientist Copeland proposed the four kingdoms of the classification system. He divided organisms into four kingdoms.
- The three-kingdom system already included the Plantae Kingdom, the Animalia Kingdom, and the Protista Kingdom. Copeland introduced another kingdom, the Monera kingdom. He also divided organisms based on body organization, separating prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic-celled organisms, such as bacteria and cyanobacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae), were moved from the Protista kingdom to the newly created Monera kingdom.
- However, a mistake remained. Plants and Fungi were still classified together in the Plantae kingdom. While there are differences between these two kingdoms, we’ll explore them further later. A newer system has been developed to address this issue.
Limitations of the Four-Kingdom System:
- It grouped plants and fungi, ignoring their distinct characteristics.
Five Kingdoms of Classification
The five-kingdom system, proposed by R.H. Whittaker, addressed the limitations of previous systems by considering five kingdoms. Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. The classification was based on five criteria:
- Body Organization: Unicellular vs. multicellular
- Cellular Structure: Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells
- Mode of Nutrition: Autotrophic vs. Heterotrophic
- Reproduction: Sexual vs. Asexual
- Phylogenetic Relationship: Evolutionary relationships
We will now explore the characteristics of each kingdom in the five-kingdom system.
Characteristics of the Five Kingdoms
Now, let’s discuss the five kingdoms and the types of organisms found in each, along with their characteristics.
Monera Kingdom
This kingdom includes organisms with prokaryotic cells. All other kingdoms contain organisms with eukaryotic cells. Examples include bacteria, blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), and mycoplasma.
Both bacteria and cyanobacteria have cell walls made of lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan, except for mycoplasma. They lack a nuclear membrane and have single-celled bodies.
Their mode of nutrition is mixed, meaning some bacteria and cyanobacteria are autotrophic (produce their food), while others are heterotrophic (obtain food from other organisms). Conjugation is a common method of reproduction in this kingdom.
Protista Kingdom
This kingdom contains single-celled eukaryotes. Only some protists have cell walls. Examples include amoebas, algae, and diatoms. They have a nuclear membrane and exhibit both autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition. Protists can reproduce sexually through gamete conjugation or asexually through conjugation.
Fungi Kingdom
This kingdom encompassed multicellular eukaryotes with cell walls made of chitin. They have a nuclear membrane. Their body structure consists of tissues but lacks organs and organ systems. Fungi are heterotrophic, obtaining nutrients by decomposing organic matter (saprotrophs) or living off other organisms (parasites). Sexually reproduction through Fertilization is the primary mode of reproduction in fungi.
Plantae Kingdom
The Plantae kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotes with cell walls made of cellulose. They possess a nuclear membrane. Their body structure is organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems. Plants are autotrophic, producing their food through photosynthesis. Fertilization is the main mode of reproduction in plants.
Animalia Kingdom
This kingdom consists of multicellular eukaryotes that lack cell walls. They have a nuclear membrane. Their body structure is most complex, with tissues organized into organs and organ systems. Animals are heterotrophic, relying on other organisms for food. Sexual reproduction through fertilization is the primary mode of reproduction in animals.
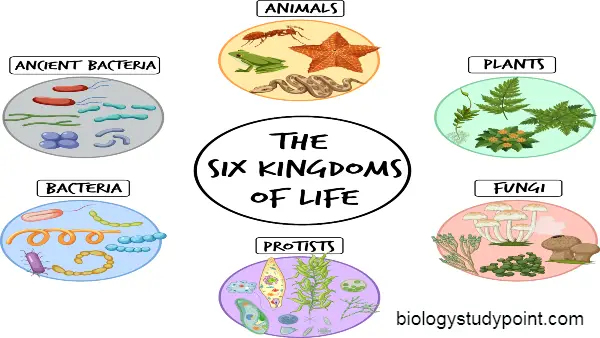
The Six Kingdoms of Classification or the Three Domains of Life
Carl Woese proposed this system after the five-kingdom system developed by R.H. Whittaker. Woese identified an issue within the Monera kingdom and divided it into two separate kingdoms.
- Archaebacteria Kingdom (Archaea): This kingdom includes archaebacteria.
- Eubacteria Kingdom: This kingdom includes bacteria.
These two new kingdoms, along with the four original kingdoms (Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia), comprise the six-kingdom classification system.
Woese also proposed a three-domain system to categorize these kingdoms:
- Archaea Domain: This domain includes archaebacteria.
- Bacteria Domain: This domain includes eubacteria.
- Eukarya Domain: This domain encompasses all organisms with eukaryotic cells, including protists, fungi, plants, and animals.
These three groups are called domains because they represent the broadest categories of life. Woese based this division on the fundamental differences in cell membranes between archaebacteria and eubacteria.
Difference Between Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
| Feature | Archaebacteria | Eubacteria |
| Cell Membrane | Two layers of lipids (bilayer), parallel | Two layers of lipids (bilayer), parallel |
| Cell Wall | Peptidoglycan absent | Peptidoglycan present |
| Cell Membrane Structure | One layer of lipids (monolayer), branched | Two layers of lipids (bilayer), parallel |
| Habitat | Extreme environments | Diverse environments |
Taxonomic Aids
Taxonomic aids are tools used for the identification, naming, and classification of organisms. Here are some examples:
- Herbarium: A collection of preserved plant specimens used for reference and identification.Herbarium sheet size: 16.5 inches x 11.5 inches
- Botanical Garden: A place where live plants are cultivated, often for conservation purposes.
- Museum: A collection of preserved plant and animal specimens of research and education. Specimens may be dried or stored in solutions like formaldehyde to prevent decay.
- Zoological Park: A place where animals are kept for exhibition, conservation, and research.
- Monograph: A detailed book about a specific taxon (e.g., a plant family or animal species).
- Flora: A book containing information about the plant life of a particular region.
- Fauna: A book containing information about the animal life of a particular region.
What is a Taxon?
If you’ve studied taxonomic hierarchy, you’d be familiar with the classification system: Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species. This is a ranking system with seven levels. Each level in this system is called a taxon (plural: taxa).
FAQs
Who is the father of taxonomy?
Carl Linnaeus is the father of taxonomy.
Who is the father of classification?
Aristotle is the father of classification.
What is the simple definition of taxonomy?
Taxonomy is the branch of biology concerned with identifying, naming, and classifying organisms.
In this article, we have provided a step-by-step explanation of the concept of taxonomy. I hope you found the information in this article helpful. If you like it, please share it with your friends.
Thank you